What are Bearings?
Bearings are mechanical components that are commonly used in machines to reduce friction and support rotating or linear motion. Bearings are designed to carry loads and provide support for the rotating components of a machine. Bearings are available in a wide range of materials, designs, and sizes.
In this guide Hi-bond, the dependable bearing and bushes suppliers, will provide an overview of the basic types of bearings and their uses.
Understanding Bearing Basics: Types of Bearings
There are several types of bearings available for different applications. Some of the most common types of bearings are:
Sleeve Bearings: Radial Load Support
Sleeve bearings, also known as journal bearings, are designed to support radial loads. Sleeve bearings are made of materials such as bronze, brass, or plastic. They are often used in applications requiring low-speed, high-load support.
Plastic Flange Bearings: Lightweight and Cost-Effective
Plastic flange bearings are designed to support light to medium radial and axial loads. They are made of plastic and are often used in applications where weight and cost are critical factors.
Ball Bearings: High Speed and Precision Applications
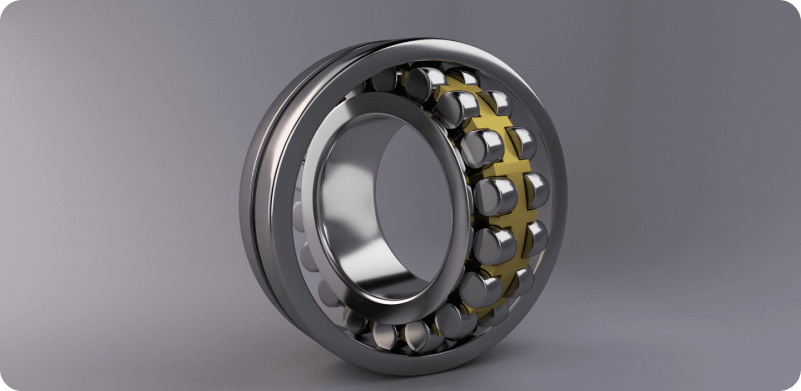
Ball bearings consist of rolling spherical elements captured between inner and outer circular races. They are ideal for machinery that requires low friction rotation, such as electric motors, pumps, and automotive components. Ball bearings are also suitable for high-speed and high-precision applications because of their standardized forms and the ease of interchangeability. There are two types of ball bearings: shielded and sealed.
Roller Bearings: Heavy Load Applications
Roller bearings are mechanical assemblies consisting of cylindrical or tapered rolling elements captured between inner and outer races. They are used in machinery that requires the support of heavier loads than ball bearings provide. Roller bearings can withstand high axial loads and have higher load capacities than ball bearings. There are different types of roller bearings, ranging from cylindrical to spherical rollers, and they are also standardized like ball bearings.
Thrust Bearings: Axial Load Support
Thrust bearings are designed to support axial loads, which are parallel to the shaft’s axis. They are used in applications where there is a need to support heavy thrust loads, such as in automotive transmissions, helicopter rotors, and marine propellers. There are different types of thrust bearings, including ball, roller, and tapered roller thrust bearings.
Mounted Bearings: Reduced Mounting Concerns
Mounted bearings are mechanical assemblies that consist of bearings housed within bolt-on or threaded mounting components, such as pillow blocks and flanged units. They provide a means of supporting rotating shafts and minimizing friction between shafts and stationary machine members. Mounted bearings are designed for ease of replacement and bolt-on mounting, making them suitable for machinery with exposed rotating shafting. They are mainly used for low and mid-speed applications and are available in different configurations, including rolling element and journal bearing.
Linear Bearings: Linear Movement and Positioning
Linear bearings consist of ball or roller elements captured in housings and used to provide linear movement along shafts. They are ideal for machinery that requires linear movement and positioning along shafts, such as robotics and automation equipment. Linear bearings offer lower friction and higher accuracy than bushings, making them suitable for high-precision applications. They also come in different designs, such as the ball bushing and the profile rail.
Slide Bearings: Structural Support and Thermal Movement
Slide bearings are mechanical assemblies designed to provide free motion in one dimension between structural elements. They are commonly used in the structural support of bridges, commercial and industrial buildings, and process equipment. Slide bearings accommodate thermal movement, allow for end-beam rotation, and isolate components of the structure against vibration, noise, and shock. They come in different types, such as those used on truss base plates and heat exchangers.
Jewel Bearings: Light Rotating Applications
Jewel bearings are mechanical devices used in light rotating applications, such as watches, meter movements, and gyroscopes, where loads are small and the supported rotating shafts are tiny. They are constructed from a range of synthetics, with ruby and sapphire being particularly common.
Frictionless Bearings: High-Precision Applications
Frictionless bearings are mechanical or electro-mechanical alternatives to conventional bearings that provide controllable shaft support through air, magnetic fields, and other means. They are ideal for critical, high-precision applications, such as aerospace, medical equipment, and semiconductor manufacturing. Frictionless bearings eliminate the need for lubrication and offer better performance in terms of speed, accuracy, and reliability.
Read More: The Facts about Flange Bearings & How They Work
Uses of Bearings:
Hi-bond offers a diverse range of bearings and bushings made from materials such as steel, copper, aluminum, and bronze, which find application across various industries., including automotive, aerospace, construction, agriculture, and many others. Let us now see various uses of bearings in different industries.
Automotive Industry
Bearings play a crucial role in the automotive industry, where they are used in a range of applications, including engines, transmissions, and wheels. In the engine, bearings support the crankshaft and camshaft, allowing them to rotate smoothly. Bearings are also used in transmissions to support the gears and shafts, allowing them to rotate freely. Wheel bearings are used to support the wheels and allow them to rotate smoothly.
Aerospace Industry
The aerospace industry uses bearings in a range of applications, including aircraft engines, landing gear, and control surfaces. Bearings used in aerospace applications must be lightweight and able to withstand extreme temperatures and loads. They are typically made from high-strength materials such as titanium or ceramic.
Construction Industry
The construction industry uses bearings in a range of equipment, including cranes, excavators, and bulldozers. Bearings are used to support the moving parts of these machines, allowing them to operate smoothly and efficiently. They are also used in conveyor belts and other equipment used in the mining and materials handling industries.
Agricultural Industry
Bearings are used extensively in the agricultural industry, where they are used in machinery such as tractors, combines, and harvesters. Bearings are used to support the moving parts of these machines, allowing them to operate smoothly and efficiently. They are also used in irrigation systems, where they support the rotating arms that distribute water across fields.
Medical Industry
Bearings are used in a range of medical equipment, including surgical instruments, X-ray machines, and MRI scanners. In surgical instruments, bearings are used to support the rotating blades, allowing them to operate smoothly and precisely. In X-ray machines and MRI scanners, bearings are used in the rotating gantry that holds the patient, allowing them to move smoothly and accurately.
How to Keep Bearings in Good Condition
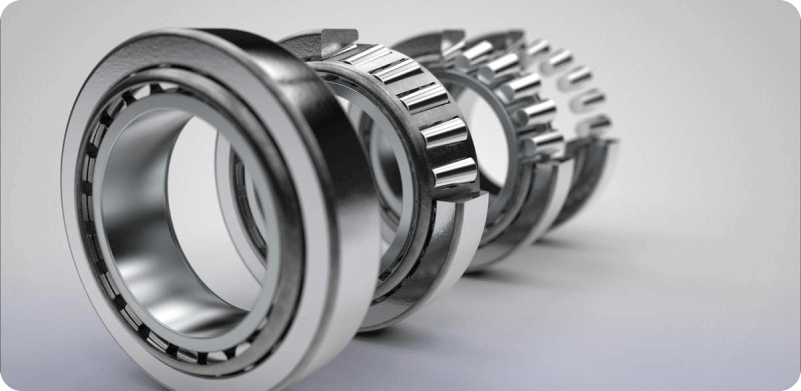
Proper maintenance is essential to keep bearings in good condition and ensure their longevity. Here are some tips on how to keep bearings in good condition:
Lubrication: Proper lubrication is critical to reduce friction between moving parts and prevent wear and tear. The type of lubricant used will depend on the bearing material and application. It is essential to follow the manufacturer’s recommendations regarding lubrication frequency and type.
Cleaning: Regular cleaning can help prevent contamination and remove debris that can cause damage to the bearing. Use a mild solvent or detergent to clean the bearing, and ensure it is completely dry before lubricating.
Alignment: Proper alignment is crucial to prevent excessive loading on the bearing and premature failure. Misalignment can cause uneven wear and increase vibration, leading to increased stress on the bearing. Regular checks of shaft alignment can prevent issues.
Temperature Control: Excessive heat can cause damage to the bearing, while cold temperatures can cause contraction and affect the lubrication. Keeping the bearing within its operating temperature range is important to ensure longevity and efficiency.
Monitoring: Regular monitoring of the bearing can detect any potential issues before they lead to failure. Vibration analysis, temperature monitoring and inspections are all useful methods of detecting potential issues before they turn into problems.
Read More: An Ultimate Guide on Thrust Bearings
Choose the Best Bearings and Bushings Manufacturers
When it comes to selecting bearings and bushings for your industrial applications, it is crucial to choose a trusted and reliable bearing manufacturing company like Hi-bond Bearings Pvt. Ltd. With years of experience in the industry, we are known for delivering high-quality bearings and bushings that are designed to meet the specific needs of different industries. Our commitment to quality, innovation, and customer satisfaction has earned us a reputation as one of the best bearing and bushing manufacturers in the market.
Whether you need bearings and bushings for automotive, aerospace, or any other industrial application, Hi-bond Bearings Pvt. Ltd has got you covered. With our extensive product range, competitive pricing, and excellent customer service, you can be confident that you are getting the best value for your investment.




