Bearings are components that allow machines to operate smoothly and efficiently. They reduce friction, support heavy loads, and ensure reliable performance across different applications, including industrial machinery. Hi-bond Bearings Pvt. Ltd discusses the complete bearing manufacturing process, revealing how these parts are crafted with precision and care. We’ll take you through each step, starting with selecting high-quality materials and moving on to the detailed assembly of every piece. You’ll also find the rigid inspection processes that ensure each bearing meets strict quality standards.
Whether you’re a seasoned professional in the industry or simply curious about engineering, this guide offers valuable insights into the bearing manufacturing process. The bearing manufacturer is committed to setting the bar for innovation and excellence in the field so that our bearings lead the way in quality and performance!
The Step-by-Step Procedure for High-Quality Bearing Production
Have you ever wondered how bearings are made? These small but essential components help the machines operate smoothly. We will mention the entire process of bearing manufacturing, from choosing the best materials to the final assembly. Each stage is important to assure that the bearings perform reliably in everything from automobiles to industrial equipment.
Step 1: Selecting Quality Raw Materials
The procedure for bearing production begins with the careful selection of high-quality raw materials. Bearing material selection such as steel, brass, and plastic are used in the process. Steel is preferred for its strength, durability, and heat resistance. Bearing manufacturers meticulously choose the right steel alloy to meet the necessary standards. The performance of bearings relies heavily on these materials, with manufacturers often opting for high-quality alloys like chrome steel or stainless steel for their excellent wear resistance and strength.
Step 2: The Forging Process
Once the materials are selected, the next step is forging. In this process, the chosen steel alloy is heated and shaped into the initial form of the bearing ring. This shaping is necessary for achieving the desired dimensions and physical properties. The blanks may undergo forging or turning techniques depending on the design requirements. Applying high pressure and temperature during forging enhances the material’s strength and structure, laying the groundwork for future steps.
Step 3: Turning and Machining Parts
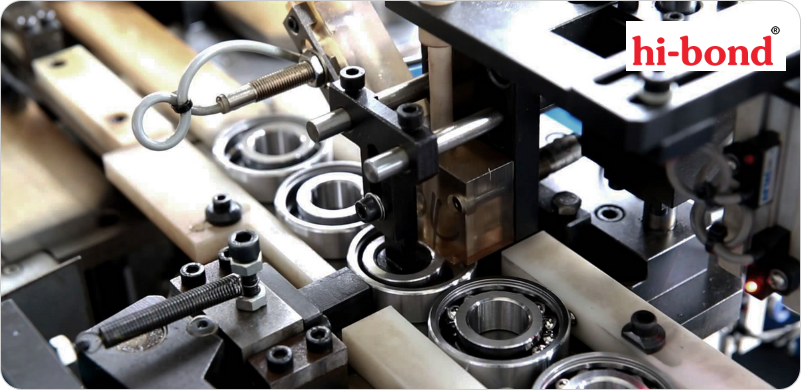
After forging, the precursor undergoes turning and machining processes. During turning, the outer and inner diameters of the rings are accurately shaped to meet specific tolerances. This precision is important for the bearings to function correctly and efficiently. Advanced CNC machines are often used to ensure exceptional accuracy during this phase. This detailed shaping technique guarantees that every component fits perfectly, contributing to the overall performance of the bearing.
Step 4: Applying Heat Treatment
Heat treatment is required in the manufacturing of bearings. The rings are subjected to techniques like quenching and tempering to enhance their hardness and durability. Achieving the proper balance of hardness is essential to withstand the forces and stresses the bearings will encounter in operation. Factors such as heating temperature and cooling rates must be carefully controlled during quenching. It ensures the final structure and hardness are ideal, preparing the bearings for their intended use.
Step 5: Grinding for High Precision
The grinding process is one of the most critical stages in bearing manufacturing. Here, the outer and inner diameters of the rings are ground to extremely tight tolerances, ensuring perfect shapes, surface finishes, and fits. Achieving this level of precision is essential to minimizing friction and improving the longevity of the bearings. With superior grinding, these components can perform well across various applications, ensuring smooth and efficient machine operation.
Step 6: Assembling the Bearing Parts
After the grinding process is complete, the various components of the bearing—including the inner ring, outer ring, rolling elements, and cage—are assembled together. This step demands a high level of precision to ensure that all parts fit perfectly without any gaps. A proper assembly is critical for the bearing’s ability to efficiently manage both radial and axial loads. Once all individual components have been machined to their specifications, they are combined to create fully functional bearing units. This process often includes press-fitting the inner and outer rings onto the rolling elements as well as adding cages or seals to protect the bearings from contaminants.
Step 7: The Role of Lubrication
Lubrication is important in minimizing friction and wear within the bearing, extending its operational lifespan. The bearing manufacturing company carefully selects appropriate lubricants that align with application requirements and operating conditions. Adequate lubrication is essential for ensuring smooth rotation as well as reducing wear on the components. During production, bearings are typically coated with high-quality lubricants, such as grease or oil. This lubrication lessens friction, helps dissipate heat, and offers protection against corrosion, providing that the bearings perform optimally over time.
Step 8: High-Grade Bearing Inspection

Inspection is the major step in the bearing manufacturing process, ensuring that each and every product meets stringent quality standards. A reputed bearing manufacturer adopts a thorough quality control approach to verify that every bearing adheres to the highest specifications. The bearing inspection process includes the following measures:
- Dimensional Checks: Measuring dimensions and tolerances of the bearing, with any discrepancies promptly corrected to maintain accuracy.
- Visual Assessments: Conduct visual inspections to detect any visible defects or surface abnormalities that may indicate damage incurred during manufacturing or issues with raw materials.
- Material Composition Analysis: Advanced bearing technology is used to analyze the material composition, ensuring conformity to required specifications.
- Hardness Evaluation: Meticulously testing the hardness of the bearing surfaces, as deviations from desired levels can significantly impact performance and durability.
- Friction and Performance Testing: Measuring friction and resistance to ensure that bearings meet necessary performance criteria for optimal functionality across various applications.
- Noise and Vibration Assessment: Performing tests to assess noise and vibration levels, confirming smooth and quiet operation, which is crucial for many applications.
- Endurance Testing: Subjecting bearings to rigorous testing under challenging conditions to evaluate their long-term performance and reliability.
- Final Visual Review: Conduct a final visual inspection to ensure the bearing is free from any surface defects or irregularities and confirm bearing products are ready for use.
Are you ready to improve your operations with top-quality bearings?
Our bearings and bushes suppliers offer a range of products with high performance and durability!
Step 9: Packaging and Dispatching
After successfully passing the rigorous inspection process, the bearings are meticulously packaged and prepared for dispatch to customers. The packaging is designed to ensure the bearings are securely contained, lowering the risk of damage during transport. Bearing manufacturers prioritize protective materials and techniques to safeguard products throughout shipping. Each package is labeled appropriately to facilitate efficient handling and delivery. A careful attention to packaging ensures that customers receive their bearings in perfect condition and ready for service.
Hi-bond Leads The Advancements in Bearing Manufacturing!

Bearing manufacturing is a detailed process that combines various steps, from choosing high-quality materials to precise machining and thorough inspections. Hi-Bond Bearings Pvt. Ltd. presents this dedication to quality and innovation, providing reliable bearings for numerous applications. Their careful engineering ensures that customers receive dependable products that meet their needs.
For example, the introduction of self-lubricating bearings is transforming the industry by lowering maintenance requirements and boosting efficiency, further highlighting the importance of high-quality bearing solutions. These developments showcase the commitment to quality in bearing manufacturing and drive progress across various industries.